Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)
Useful For
Investigation of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)
Indications for IGRA testing
| 1 | When the risk of infection, of progression to disease and of a poor outcome are high |
| 2 | When false-negative or false-positive Tuberculosis Skin Test (TST) results are suspected |
| 3 | People who have received BCG as a vaccine after infancy (1 year of age) and/or have received BCG vaccination more than once. |
| 4 | People from groups that historically have poor rates of return for TST reading. |
| 5 | In children with suspected TB disease, IGRAs may be used as a supplementary diagnostic aid in combination with the TST and other investigations to help support a diagnosis of TB. However, IGRA should not be a substitute, or obviate the need, for appropriate specimen collection. A negative IGRA does NOT rule out active TB at any age and especially not in young children. |
| 6 | Repeating an IGRA might be useful when the initial TST result is indeterminate, borderline or invalid and a reason for testing persists. |
Situations in which IGRA should NOT be used for testing
| 1 | Active TB diagnosis in adults |
| 2 | Repeat testing in a contact investigation, or serial testing of health care or other populations (e.g. corrections staff or prison inmates) with potential for ongoing exposure |
| 3 | Routine or mass screening for LTBI of all immigrants (adults and children) |
| 4 | Monitoring anti-TB treatment response |
| 5 | LTBI screening pre-biologic treatment |
Method Name
Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)
Enzyme linked immunoassay (ELISA)
Reporting Name
IFN-gamma
Aliases
LTBI
Latent tuberculosis infection
Quantiferon
IGRA
Interferon gamma release assay
QFT-Plus
Specimen Requirement
| Test requested | Specimen Type | Minimum Volume | Collection Kit |
| Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) | Whole blood | 1 ml directly into each of the four blood collection tubes. Total volume 4 ml.
|
· QuantiFERON Nil control (grey cap)
· QuantiFERON TB1 tube (green cap) · QuantiFERON TB2 tube (green cap) · QuantiFERON Mitogen control (purple cap) |
Reject Due To
| Specimens other than QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus blood collection tubes |
| Mislabeled, unlabeled, leaking blood collection tubes |
| Specimens received >16 hours post collection without proper incubation and centrifugation |
Special Instructions
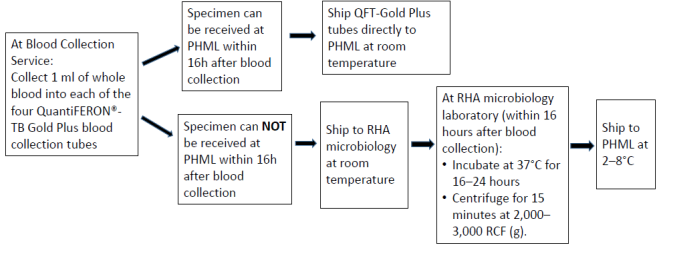
Quantiferon Collection and shipping instructions
Note:
- If the blood is not incubated immediately after collection, remixing of the tubes by inverting 10 times must be performed immediately prior to incubation.
- Tubes must be incubated within 16 hours of collection
Clinical Information
When a subject is exposed to M. tuberculosis and infection occurs, the infection may either progress to active tuberculosis (TB) disease, defined as signs, symptoms and/or laboratory abnormalities indicating tissue destruction, or remain in a subclinical asymptomatic state known as latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). The main purpose of diagnosing LTBI is to consider medical treatment for preventing tuberculosis disease.
Diagnosis or excluding tuberculosis disease, and assessing the probability of LTBI, requires a combination of epidemiological, historical, medical and diagnostic findings that should be considered when interpreting QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus results.
Interpretation
| Result | Interpretation |
| Positive | M. tuberculosis infection likely |
| Negative | M. tuberculosis infection NOT likely |
| Indeterminate | Likelihood of M.tuberculosis infection cannot be determined |
A positive QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus result should be followed by further medical evaluation and diagnostic evaluation for active tuberculosis disease (e.g., AFB smear and culture, chest x-ray).
· A positive result should not be the sole or definitive basis for determining infection with M. tuberculosis. Incorrect performance of the assay may cause false positive responses.
· While ESAT-6 and CFP-10 are absent from all BCG strains and from most known nontuberculous mycobacteria, it is possible that a positive QFT-Plus result may be due to infection by M. kansasii, M. szulgai, or M. marinum. If such infections are suspected, alternative tests should be performed.
A negative QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus result does not preclude the possibility of M. tuberculosis infection or tuberculosis disease. False-negative results can be due to
· Stage of infection (e.g., specimen obtained prior to the development of cellular immune response).
· Co-morbid conditions which affect immune functions. The predictive value of a negative QFT-Plus result in immunosuppressed persons has not been determined.
· Incorrect handling of the blood collection tubes following venipuncture, incorrect performance of the assay, or other immunological variables.
· Heterophile antibodies or non-specific IFN-γ production from other inflammatory conditions may mask specific responses to ESAT-6 or CFP-10 peptides.
An indeterminate QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus result may relate to:
· The immune status of the individual being tested
· Incorrect transport/handling of blood specimen
· Elevated levels of circulating IFN-γ or presence of heterophile antibodies
Reference
QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus: package insert. Qiagen, USA, 2018
Canadian Tuberculosis Standards 7th Ed. 2014.
| Status | Test Frequency | Turnaround Time (TAT) |
| Routine | Once weekly | 7 days after the receipt by PHML |
Method Description
The QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus test is an in-vitro diagnostic test for latent TB infection. It measures T cells (both CD4 T and CD8 T cells) release of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) following stimulation by peptides from TB antigens (ESAT-6 and CFP-10). These antigens are absent from all BCG strains and from most nontuberculosis mycobacteria with the exception of M. kansasii, M. szulgai and M. marinum.
Performing Laboratory Location
Public Health Microbiology Laboratory
St. John’s
Newfoundland & Labrador